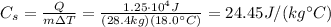Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
The heat added to the sample is related to its increase in temperature by:
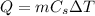
where
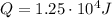 is the heat added
is the heat added
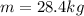 is the mass of the sample
is the mass of the sample
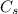 is the specific heat
is the specific heat
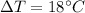 is the increase in temperature
is the increase in temperature
Substituting the numbers into the equation, we find the specific heat: