Answer:
C.The solution n = 0 is an extraneous solution.
Explanation:
The given equation is
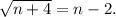
Squaring both sides we have:
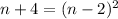
Expanding the right side:
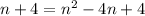
Or ,
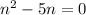
n(n-5)=0
n=0 or n=5.
Checking the solution for n=0 in the above equation:
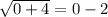 False .
False .
For n=5.
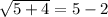
True.
C.The solution n = 0 is an extraneous solution.