Answer:
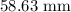
Step-by-step explanation:
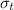 = True stress = 415 MPa
= True stress = 415 MPa
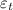 = True strain = 0.475
= True strain = 0.475
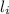 = Original length of the alloy = 300 mm
= Original length of the alloy = 300 mm
Let us assume n = Strain hardening component = 0.25
K = Constant
True stress is given by
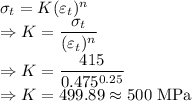
Now
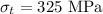
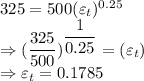
True strain is given by
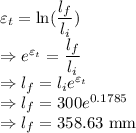
Elongation of material is
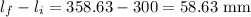 .
.