Answer:
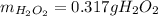
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello!
In this case, for the chemical reaction between hydrochloric acid and barium peroxide is:
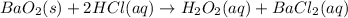
Thus, since the barium peroxide (169.33 g/mol) and hydrochloric acid (36.45 g/mol) are reacting in a 1:2 mole ratio, we need to identify the limiting reactant first by computing the yielded moles of hydrogen peroxide by each reactant:
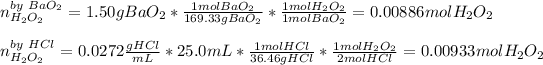
That's why the HCl is the limiting reactant, so the resulting mass of hydrogen peroxide, theoretical yield, is:
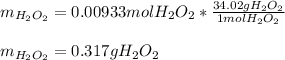
Best regards!