Answer:
Correct option is 1st option
Explanation:
1. The theoretical probability is a ratio of the number of favorable outcomes to the number of possible outcomes,
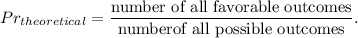
2. The experimental probability is the ratio of the number of times an outcome occurs to the total number of times the activity is performed,
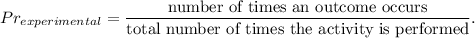
3. In your case, the experimental probability (from the table) is
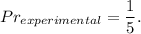
Note that a bag contains 5 tiles in total, one yellow tile among them, then
- number of favorable outcomes = 1;
- number of all possible outcomes = 5
and

Thus, the experimental probability is the same as the theoretical probability