1. Parabola
The path taken by a projectil is known as parabola, and it consists of two independent motions:
- along the horizontal direction, it is a uniform motion with constant speed
- along the vertical direction, it is an accelerated motion with constant acceleration, g=9.8 m/s^2 downward
2. A person sitting in a chair, not moving
This is NOT a motion of a projectile. In fact, the person is not moving at all, so this is not a motion.
3. 490 meters
The supplies will move of uniform accelerated motion, with constant acceleration g=9.8 m/s^2, so the distance they cover is given by
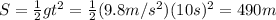
4. 65 m/s
The horizontal motion of the supplies is a uniform motion, with constant speed equal to the ratio between the horizontal distance covered and the time taken:
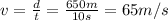
5. True
As explaned in exercise 1), a projectile has two independent motions: one along the horizontal direction and one along the vertical direction. Therefore, it also has a horizontal component of the velocity (which is constant) and a vertical component of the velocity (which changes because there is an acceleration acting along this direction)
6. False
As stated in exercise 1) and 2) the trajectory of a projectile is a parabola, not an ellipse.
7. The vertical component always equals the horizontal component
This statement is not true: as we said, the horizontal component of the velocity is constant, while the vertical component constantly changes, so they cannot be always equal (in fact, they will be equal only at some precise instant of the motion)
8. constant
As stated before, there is no force acting along the horizontal direction of the projectile's motion, so the horizontal acceleration is zero, and this means that the horizontal velocity is constant.
9. Vertical velocity decreases.
When the projectile is moving upward, its vertical velocity decreases, because the acceleration (which acts downward) acts in the opposite direction of the velocity. More specifically, the vertical velocity is given by
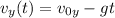
where v0y is the initial vertical velocity of the projectile, t is the time and g=9.8 m/s^2.
10. Vertical velocity increases.
When the projectile is moving downward, its vertical velocity increases, because the acceleration (which acts downward) this time is acting in the same direction of the velocity