The correct answer to the question is : 19.6 N.
EXPLANATION :
As per the question, the mass of the object m = 2.0 Kg.
The object is falling near the earth's surface.
We are asked to calculate the gravitational force.
The gravitational force exerted by earth on the object is equal to the weight of the body. It is so because the weight of the body is the force with which any body on the surface of earth is attracted towards the centre of earth.
The weight of the body is calculated as-
Weight W = mg
Here, g is known as the acceleration due to gravity and g =
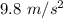
Hence, weight of the body W = 2 × 9.8 N.
= 19.6 N.
Hence, the gravitational force on the object is 19.6 N.