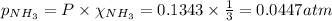Step-by-step explanation:
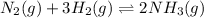
c) Concentration of
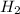 in this mixture
in this mixture
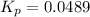
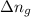 :
:
=(gaseous mole on product side)-(gaseous mole on reactant side)=2-4=-2
R = 8.314 J/mol K
T = 256 °C = 256+273 = 529 K
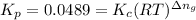
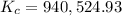
![K_c=940,524.93=([NH_3]^2)/([N_2][H_2]^3)=((0.0300 mol/L)^3)/(0.0100 mol/L* [H_2]^3)](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/college/tcxeec5cfybbcng443q6yiheh9jf36ctu6.png)
![[H_2]^3=10,450,277](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/college/rjxoe3ze8tky6vagrjx2helh57oz01nerf.png)
![[H_2]=218.62 mol/L](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/college/8m0wpx8r3de2ipqb886ski7tfih7ugbi09.png)
The concentration of hydrogen gas is 218.62 mol/L
d)A fourth equilibrium mixture contains equal concentrations of all three chemicals
![[N_2]=[H_2]=[NH_3]=x mol/L](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/college/xihb04qw6obzgz6sk52pt8c7j5fu7t5kru.png)
![K_c=940,524.93=([NH_3]^2)/([N_2][H_2]^3)=(x^2)/(x* x^3)=(1)/(x^2)](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/college/675292xwpq5n8osdkcxa64hlwfd38r5clu.png)
x =
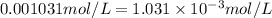
According ideal gas equation:
PV=nRT
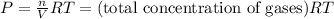
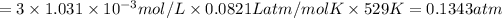
Total pressure,P = 0.1343 atm
Partial pressure of nitrogen gas
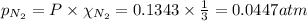
Partial pressure of hydrogen gas
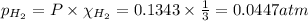
Partial pressure of ammonia gas