Answer:-
![([In^-])/([HIn])=3.16*10^-^8](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/college/940qsturv9cqowarsikyeosyvwdrpfsbca.png)
Solution:- If both acid and basic form are present at the same time then it's like a buffer solution since the buffer solution also has a weak acid and its conjugate base. The Handerson equation is used for solving buffer problems. Let's use the same equation here also.
The equation is:
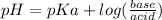
pKa is given as 9.7 and the pH is 2.2. let's plug in the values in the equation.
![2.2=9.7+log(([In^-])/([HIn]))](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/college/ksbq2q9tw8i77ftct60sv2pmmxe3ns6b8f.png)
subtract 9.7 from sides:
![2.2-9.7=log(([In^-])/([HIn]))](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/college/zp4hwz03sqfs5vwzsfrf3tzoq3x8wswtu0.png)
![-7.5=log(([In^-])/([HIn]))](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/college/tpvf1gin0y25kn4lkth98zrki8gu46bj26.png)
taking antilog:
![10^-^7^.^5=([In^-])/([HIn])](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/college/ehfvaxamflu6voh8gwyx4o6ikewtuovmme.png)
![3.16*10^-^8=([In^-])/([HIn])](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/college/zg08y1k8etu47j5q10w3h0cq3hywyra8a2.png)
So, the answer is
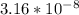 .
.