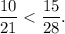Consider two fractions
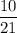 and
and
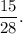
1. Approximate first fraction by
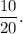 You know that
You know that
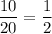 and comparing two fractions with the same numerators, we compare their denominators. Since
and comparing two fractions with the same numerators, we compare their denominators. Since
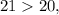 then
then
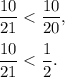
2. Approximate the second fraction by
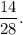 You know that
You know that
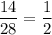 and comparing two fractions with the same denominators, we compare their numerators. Since
and comparing two fractions with the same denominators, we compare their numerators. Since
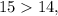 then
then
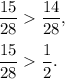
You have two fractions, the first one is less than
 and the second one is greater than
and the second one is greater than
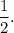 Thus,
Thus,
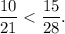
Answer: