Answer: ionization energy
Step-by-step explanation:
Ionization energy is the energy required to remove the most loosely bound electron from a gaseous atom.
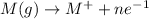
Metals have low ionization energy as they tend to attain stable configuration by losing the valence electrons. Example: Sodium
Nobles gases have high ionization energy as they do not tend to lose electrons easily due to their high stability.
In a group, the ionization energy decreases as we move down as the size increases and thus the valence shell moves farther from nucleus and thus is easier to remove.
In a period, the ionization energy increases as we move across, the size decreases and thus the valence shell moves near to the nucleus and thus it gets difficult to remove.