Answers:
Vertical asymptote: x = 0
Horizontal asymptote: None
Slant asymptote: (1/3)x - 4
Step-by-step explanation:
d(x) =
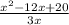
=
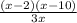
Discontinuities: (terms that cancel out from numerator and denominator):
Nothing cancels so there are NO discontinuities.
Vertical asymptote (denominator cannot equal zero):
3x ≠ 0
÷3 ÷3
x ≠ 0
So asymptote is to be drawn at x = 0
Horizontal asymptote (evaluate degree of numerator and denominator):
degree of numerator (2) > degree of denominator (1)
so there is NO horizontal asymptote but slant (oblique) must be calculated.
Slant (Oblique) Asymptote (divide numerator by denominator):
- (1/3)x - 4
- 3x) x² - 12x + 20
- x²
- -12x
- -12x
- 20 (stop! because there is no "x")
So, slant asymptote is to be drawn at (1/3)x - 4