Answer:- cell potential = -0.19 volts
Solution:- The equation that shows the connection between
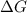 and cell potential, E is written as:
and cell potential, E is written as:
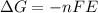
in this equation, n stands for moles of electrons, E stands for cell potential and F stands for faraday constant and it's value is
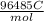 .
.
It asks to calculate the value of E, so let's rearrange the equation:
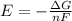
Let's plug in the values in it:

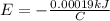
since,
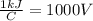
Where C stands for coulombs and V stands for volts.
So,
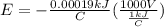
E = -0.19 V
So, the cell potential is -0.19 volts.