Answer:
11 people
Explanation:
Mean body temperature = u = 37.0 degrees
Standard Deviation =
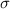 = 0.35 degrees
= 0.35 degrees
Sample Size = n = 148
We have to find how many people in a sample of 148 will have body temperatures above 37.5 degrees. For this first we need to find what is the percentage of people with body temperatures above 37.5 degrees. This can be done by converting 37.5 to equivalent z score and using z table to find what percentage would be above that value.
The formula for z score:
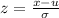
Using the values, we get:
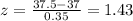
So now from z table we have to find what is the percentage of the z score being above 1.43, which comes out to be 0.0764 or 7.64%
This means, 7.64% of people will have body temperatures above 37.5 degrees. This means from a sample of 148, number of people with body temperatures above 37.5 degrees would be:
7.64 % of 148 = 0.0764 x 148 = 11 (rounded to nearest integer)
11 people are expected to have the body temperatures above 37.5 degrees