(1)
distribute parenthesis on both sides of the equation and simplify
10r - 30 = 4r + 52 - 10r - 50
10r - 30 = - 6r + 2 ( add 6r to both sides )
16r - 30 = 2 ( add 30 to both sides )
16r = 32 ( divide both sides by 16 )
r = 2
(2)
distribute parenthesis
- 0.5x + 5 < 12 ( subtract 5 from both sides )
- 0.5x < 7
divide both sides by - 0.5, remembering to reverse the inequality symbol as a consequence
x > - 14 → (C)
(3)
obtain the equation of the line in slope-intercept form
y = mx + c ( m is the slope and c the y-intercept )
calculate the slope using the gradient formula
m = (y₂ - y₁ ) / (x₂ - x₁ )
with (x₁, y₁ ) = (0, 2) and (x₂, y₂ ) = (3, - 3 ) ← 2 points on the line
m =
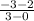 = -
= -
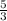
the y-intercept = (0, 2 ) ⇒ c = 2
y = -
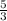 + 2 ← equation of line
+ 2 ← equation of line
the shaded area ( the solution ) is below the line which is solid, thus
y ≤ -
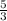 x + 2 → (B)
x + 2 → (B)
(4)
This data can only be a function if each value of x maps to exactly one value of y
The only values satisfying this criteria are B, C and D
as 0 → 1 and - 3 → - 1 so cannot map to other values of y