Answer:
15 g
Step-by-step explanation:
Specific Heat Capacity
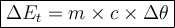
Where:
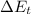 = Change in thermal energy measured in joules (J).
= Change in thermal energy measured in joules (J).- m = Mass measured in kilograms (kg).
- c = Specific heat capacity measured in joules per kilogram per degree Celsius (J/kg°C)
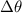 = Temperature change measured in degrees Celsius (°C).
= Temperature change measured in degrees Celsius (°C).
Given:
As the specific heat capacity is given in J/g°C, the temperature is given in °C, and the mass is in grams, no conversion of units is necessary.
Substitute the values into the formula and solve for m:
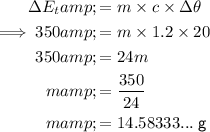
Therefore, the mass of the substance is 15 g (nearest whole number).