Remember what L'Hospital's Rule tells us. It says the following.
If
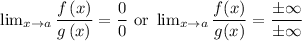
Then
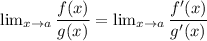
We know that
 using direct substitution and
using direct substitution and
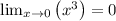 through direct substitution as well. Thus, we can find the derivatives of the numerator and denominator and find our limit.
through direct substitution as well. Thus, we can find the derivatives of the numerator and denominator and find our limit.
![(d)/(dx)[x - \sin x] = 1 - \cos x](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/mathematics/middle-school/wjf6il4ugtjvdjm2zio7h9lelc7tsrtggc.png)
![\frac {d}{dx}\left[ x^(3)\right] =3x^(2)](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/mathematics/middle-school/1dgcyhp4ne3cm9ynj7nl0q206d419vpzlg.png)
Thus, we are now trying to find:
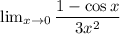
To do this, we can use direct substitution for both the numerator and denominator.
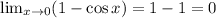
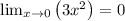
Again, we have the following:
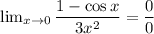
Thus, we are going to have to use L'Hospital's Rule again.
![\frac {d}{dx}\left[ 1-\cos x\right] =\sin x](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/mathematics/middle-school/eht1tltry3qwfze2vf9bjvehd3uafzikl8.png)
![\frac {d}{dx}\left[ 3x^(2)\right] =6x](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/mathematics/middle-school/60vyf1vsglkf0dqe1e3arph3wkigskbooa.png)
Now, we are trying to find the following:
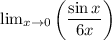
Let's find the limits of the numerator and denominator and set them over each other to find the answer to this limit.
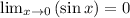
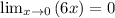
Again, we are going to have to L'Hospital's Rule to find the limit since the answer to our limit is:
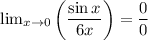
![\frac {d}{dx}\left[ \sin x\right] =\cos x](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/mathematics/middle-school/r8ykvb7fy2r35b4jvf62vx4gdvx9kjy8tw.png)
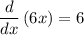
Now, we are trying to find:
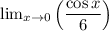
We are going to use direct substitution to find the limits of the numerator and denominator to find the answer.
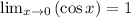
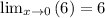
Thus, the answer to this limit is:
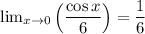
Our answer is 1/6.