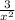Answer:
see explanation
Explanation:
Given f(x) then the derivative f'(x) is
f'(x) = lim( h tends to 0 )
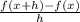
= lim( h to 0 )
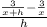
= lim( h to 0 )
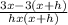
= ( lim h to 0 )
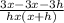
= lim( h to 0 )
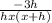 ← cancel h on numerator/ denominator
← cancel h on numerator/ denominator
= lim( h to 0 )
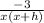 ← let h go to zero, then
← let h go to zero, then
f'(x) = -