The answer to the question will be 108.76 N.
CALCULATION:
The mass of the ball is given as m = 0.17 kg.
The initial speed of the ball [ u ] = 37.9 m/s.
The momentum of a body is defined as the product of its mass with velocity.
Mathematically momentum P = m × v.
Here, v is the velocity of the body.
Hence, the initial momentum of the ball is calculated as -
P = m × u
= 0.17 kg × 37.9 m/s
= 6.443 kg m/s
The ball returns after striking the bat with a speed of 20.0 m/s.
Hence, the final velocity of the ball [ v ] = 20.0 m/s
The final momentum of the ball is calculated as -
P' = m × v
= 0.17 kg × (-20.0 m/s)
= -3.4 kg m/s.
Here, the negative sign used in the velocity is due to the fact that final velocity is opposite to the initial velocity.
Hence, the change in momentum dP = P' - P
= -3.4 - 6.443 kg m /s
= -9.843 kg m/s
The time of contact of the bat with ball [ dt ] = 90.5 milliseconds.
=
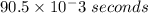
From Newton's second law of motion, we know that rate of change of momentum is directly proportional to the applied force and takes place along the direction of force.
Mathematically
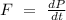
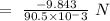
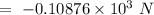
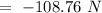
Taking only magnitude of the force, the force applied by the bat to the ball is 105.78 N.