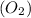A chemical change occurs when reactants undergo molecular or ionic rearrangements of atoms to form new substances. This is facilitated by the breakage of bonds which require consumption of energy and making of bonds which release energy.
For instance, when sodium reacts with water there is a vigorous reaction that produces sodium hydroxide NaOH and hydrogen gas (
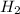 )
)
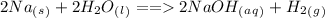
Clearly the molecules of
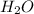 bonds are broken to make bonds with Na and form NaOH and H₂.
bonds are broken to make bonds with Na and form NaOH and H₂.
Another example
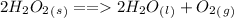
In this case hydrogen peroxide gets broken down
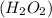
to form water
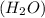 and oxygen
and oxygen