Answer:
-61
by both methods
Explanation:
Let's first see what the terms direct substitution and synthetic substitution mean.
Direct Substitution
In direct substitution, to find the value of a polynomial f(x) at any point x = k. we simply substitute the value of k into the polynomial function and solve for f(k)
Synthetic Substitution
In synthetic substitution we make use of the Remainder Theorem..
The Remainder Theorem states that when we divide a polynomial
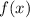 by
by
 , the remainder
, the remainder
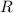 equals
equals
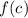
Solving using direct substitution
The given polynomial is
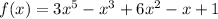
and we are asked to evaluate this function at

Using Direct Substitution,
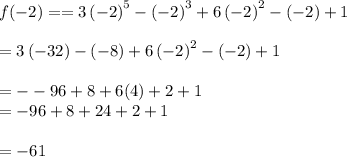
Using direct substitution we get
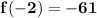
Using Synthetic Substitution
Since the remainder when
 is divided by
is divided by
 is
is
 , we will divide the polynomial
, we will divide the polynomial
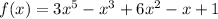 by
by
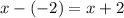 and find out the remainder which will give f(-2)
and find out the remainder which will give f(-2)
This is the technique used in synthetic division
Step 1. Write only the coefficients of
 in the dividend inside an upside-down division symbol. Write -2 as the divisor on the left of this row
in the dividend inside an upside-down division symbol. Write -2 as the divisor on the left of this row
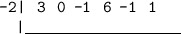
Step 2
Carry down the leading coefficient as is to below the division symbol
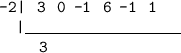
Step 3
Multiply the above carry-down value by -2 and carry that result to the next column:
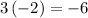
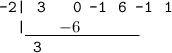
Step 4
Add down the column
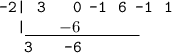
Step 5
Multiply the above carry-down value by -2 and carry that result to the next column:
(-6)(-2) = 12
2 | 3 0 -1 6 -1 1
| -6 12
-------------------------------------------------
3 -6
Step 6
Add down the column
-1 + 12 = 11
2 | 3 0 -1 6 -1 1
| -6 12
-------------------------------------------------
3 -6 11
Repeat this process for the other two coefficients
The final result is
2 | 3 0 -1 6 -1 1
| -6 12 -22 32 -62
-------------------------------------------------
3 -6 11 -16 31 -61
The last carry-down value s the remainder and the value of f(-2) = - 61