using ( f ○ g )(x) = f(g(x))
substitute x =
 into f(x)
into f(x)
f(g(x)) = 5 / (
 + 2 ) ×
+ 2 ) ×

=

=
 =
=

The denominator of f(g(x)) cannot be zero as this would make f(g(x)) undefined. Equating the denominator to zero and solving gives the value that x cannot be
solve 2x + 3 = 0 ⇒ x = -
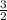 ← excluded value
← excluded value
domain is x ∈ ( - ∞, -
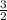 ) ∪ ( -
) ∪ ( -
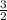 , + ∞ )
, + ∞ )