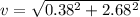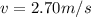Answer:
So after collision 2nd ball will move off with speed 2.70 m/s
Step-by-step explanation:
When two balls of equal mass collides elastically then after collision the two balls will move away at some angle with respect to each other
Here we know that the first ball is moving with speed 3 m/s initially and after collision it moves off by 50 degree with speed 0.50 m/s
so here we can say by momentum conservation
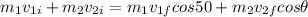
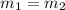
so we will have
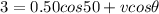
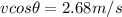
Similarly in perpendicular direction we have
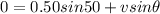
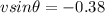
so net speed of the ball is given as