Answer:
For the given coordinates of vertex C of Option A and Option C ,△ABC is a right triangle.
Explanation:
Coordinates of A = (−2,4)
Coordinates of B =(−1,1)
Since we are asked For each of the given coordinates of vertex C, is △ABC a right triangle
So, Option 1)
Coordinates of C = (2,2)
Now to find length of AB, BC and AC
Distance formula:
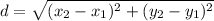
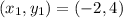
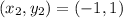
Substitute the vales in the formula
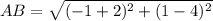
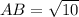
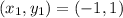
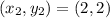
Substitute the vales in the formula
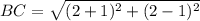
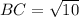
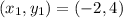
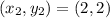
Substitute the vales in the formula
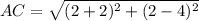
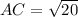
So,
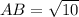 ,
,
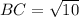 and
and
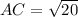
Now to check whether it is a right angled triangle or not
We will use Pythagoras theorem
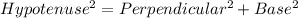
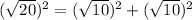
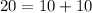
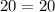
So, For Option 1 , △ABC is a right triangle.
Option 2)
Coordinates of C = (0,4)
Now to find length of AB, BC and AC
Distance formula:
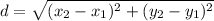
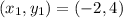
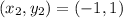
Substitute the vales in the formula
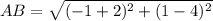
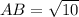
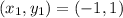
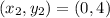
Substitute the vales in the formula
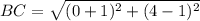
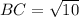
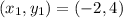
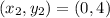
Substitute the vales in the formula
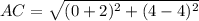
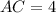
So,
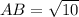 ,
,
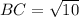 and
and
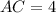
Now to check whether it is a right angled triangle or not
We will use Pythagoras theorem
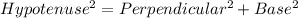
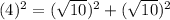
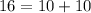
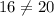
So, For Option 2, △ABC is not a right triangle.
Option 2)
Coordinates of C = (-2,1)
Now to find length of AB, BC and AC
Distance formula:
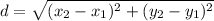
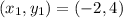
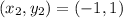
Substitute the vales in the formula
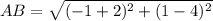
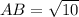
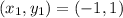
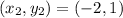
Substitute the vales in the formula
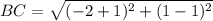
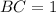
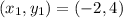
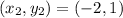
Substitute the vales in the formula
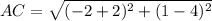
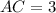
So,
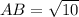 ,
,
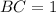 and
and
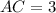
We will use Pythagoras theorem
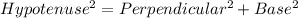
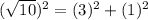
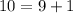
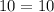
So, For Option 3, △ABC is a right triangle.
Hence For the given coordinates of vertex C of Option A and Option C ,△ABC is a right triangle.