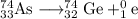Answer:
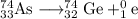
Step-by-step explanation:
The unbalanced nuclear equation is
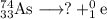
It is convenient to replace the question mark by an atomic symbol,
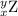 , where x = the atomic number, y = the mass number, and Z = the symbol of the element .
, where x = the atomic number, y = the mass number, and Z = the symbol of the element .
Then your equation becomes
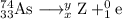
The main point to remember in balancing nuclear equations is that **the sums of the superscripts and the subscripts must be the same on each side of the equation**.
Then
74 = x + 0, so x = 74
33 = y + 1, so y = 33 -1 = 32
Element 33 is germanium, so the nuclear equation becomes