Answer:- 10.6 L.
Solution:- Temperature is not given in this problem so it must be constant and we know that at constant temperature, the volume of the gas is inversely proportional to it's pressure. It is Boyle's law.
The equation for this law is written as:
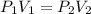
P stands for pressure and V stands for volume and the subscripts 1 and 2 are representing initial and final values.
Initial pressure is 845 mmHg, initial volume is 4.60 L. Final volume is 368 mmHg and it asks to calculate the final volume.
Let's plug in the values in the equation and solve it for final volume.
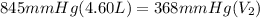
divide both sides by 368mmHg:
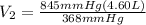
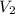 = 10.6 L
= 10.6 L
So, the gas is transferred to a container with a volume of 10.6 L.