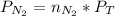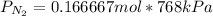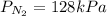Answer:
256kPa
Step-by-step explanation:
You can find the partial pressure applying the Dalton´s law of partial pressure, that is:
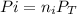
where
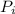 is the partial pressure of each gas,
is the partial pressure of each gas,
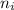 is the molar fraction of the gas and
is the molar fraction of the gas and
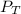 is the total pressure.
is the total pressure.
To found these values, first of all you should find the molar fraction of each gas:
For
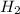 :
:
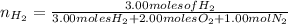
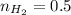 moles of
moles of
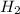
For
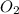 :
:
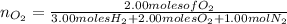
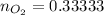 moles of
moles of
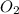
For
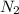 :
:
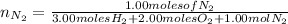
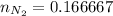 moles of
moles of
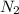
Then you can apply the Dalton´s law, replacing the values for the molar fraction :
For
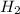 :
:
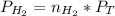
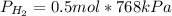
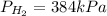
For
 :
:
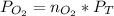
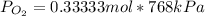
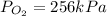
For
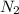 :
: