Answer:
Red giant
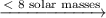 white dwarf ⟶ black dwarf
white dwarf ⟶ black dwarf
Red giant
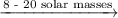 supernova ⟶ neutron star
supernova ⟶ neutron star
Red giant
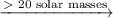 supernova ⟶ black hole
supernova ⟶ black hole
Step-by-step explanation:
Low-mass Stars
As the core of a red giant collapses collapses, the outer layers are expelled to form a planetary nebula, while the core becomes a white dwarf.
The white dwarf cools to form a black dwarf.
High-mass stars
As high-mass stars collapse, their core temperatures increase as carbon fuses to form heavier elements, ending with the most stable one, iron.
Gravitational collapse crushes the iron atoms together. Nuclear repulsions overcome the force of gravity and the star erupts in a massive supernova explosion.
If the star has 8 to 20 solar masses, the remnant will collapse of its own gravity and become a neutron star.
If the star has more than 20 solar masses, the force of gravity is so great that the remnant collapses to a black hole.