Answer:- Heat lost by the metal is 279.45 cal.
Solution:- This type of problems are solved by using the concept, heat given = - heat taken
Metal temperature is decreasing from 45.00 degree C to 11.08 degree C. It means the heat is lost by the metal and this heat lost by metal is gained by water and the calorimeter to raise their temperature.
the equation we use is,
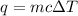 .
.
where, q is the heat energy, m is mass, c is specific heat and
 is change in temperature.
is change in temperature.
Combined mass of calorimeter and water is 250.0 g and the specific heat is
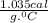 .
.
 for calorimeter and water (combined) = 11.08 - 10.00 = 1.08 degree C
for calorimeter and water (combined) = 11.08 - 10.00 = 1.08 degree C
 for metal = 11.08 - 45.00 = -33.92 degree C
for metal = 11.08 - 45.00 = -33.92 degree C
let's plug in the values in the above equation and calculate heat gained by combined system.
q=250.0g*\frac{1.035cal}{g.^0C}*1.08^0C
q = 279.45 cal
So, the heat lost by the metal is 279.45 cal.