In the Slope-Intercept Form, m is the slope and b is the y-intercept.
Finding The Equation of a Line Parallel to the Given Line: Let the given line be line a and the parallel line be line b.
1) Find the slope of line a.
Example: Line a -->
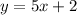 . The slope is 5.
. The slope is 5.
2) Find the y-intercept of line b.
To do this, you need to be given the coordinates of a point located on line b.
Example: The slope is 5 and the point is (2, 3), use the Slope-Intercept Formula,
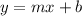 --->
--->
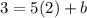 . Then you solve for b.
. Then you solve for b.
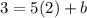
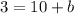
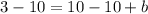
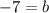
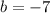
The y-intercept of line b is -7
3) Finally, plugin the slope and the y-intercept into the Slope-Intercept Form.
Example: The slope of line b is 5 and the y-intercept is -7. The equation of line b is
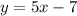 .
.
Finding The Equation of a Line Perpendicular to The Given Line: Let the given line be line a and the perpendicular line be line b.
1) Find the opposite reciprocal of the slope of line a.
Example: Line a -->
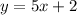 . The slope is 5, to find the opposite reciprocal of the slope you use n -->
. The slope is 5, to find the opposite reciprocal of the slope you use n -->
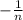 . In this case, it would be
. In this case, it would be
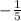 . The opposite reciprocal of the slope of line a is
. The opposite reciprocal of the slope of line a is
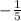 , which would be the slope of line b.
, which would be the slope of line b.
2) Find the y-intercept of line b.
To do this, you need to be given the coordinates of the point where line a and line b both intersect.
Example: The slope of line b is
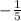 and the point is (1, 7), use the Slope-Intercept Formula,
and the point is (1, 7), use the Slope-Intercept Formula,
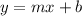 --->
--->
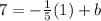 . Then you solve for b.
. Then you solve for b.
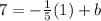
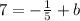
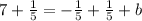
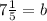
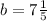
The y-intercept of line b is
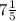 .
.
3) Finally, plugin the slope and the y-intercept into the Slope-Intercept Form.
Example: The slope of line b is
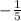 and the y-intercept is
and the y-intercept is
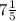 . The equation of line b is
. The equation of line b is
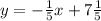 .
.