Answer:
Co(NO₃)₂·6H₂O
Step-by-step explanation:
Assume that you have 100 g of the hydrate.
Then you have 62.9 g Co(NO₃)₂ and 37.1 g H₂O.
1. You will need a chemical equation with masses and molar masses, so let’s gather all the information in one place.
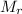 : 182.94 18.02
: 182.94 18.02
Co(NO₃)₂·xH₂O ⟶ Co(NO₃)₂ + xH₂O
Mass/g: 62.9 37.1
2. Use the molar masses of each compound to calculate its number of moles.
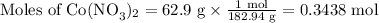
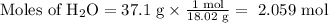
3. Calculate the molar ratio of the two products.
Divide each number by the smaller number of moles (0.3438 mol).

4. Round off each number to the closest integer.
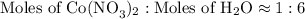
1 mol of Co(NO₃)₂ combines with 6 mol H₂O, so x = 6.
The formula of the hydrate is Co(NO₃)₂·6H₂O.