Answer:
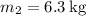
Step-by-step explanation:
In a perfectly elastic collision, the total kinetic energy of the system is maintained. Therefore, we can set up the following equation:
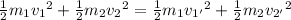
Since the second block was initially at rest,
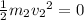 .
.
Plugging in all given values, we have:
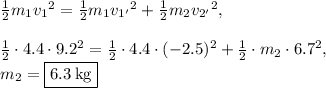 .
.