Answer : The pH of the solution will be 13.63.
Solution:
Moles of hydroxide ions in barium hydroxide solution
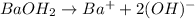
Number of moles = (concentration)
 (volume in liters) ...(1)(1L=1000mL)
(volume in liters) ...(1)(1L=1000mL)
2.0 M barium hydroxide in solution
Number of moles of
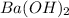 in 2.0 M solution
in 2.0 M solution
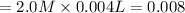 moles
moles
If One mole of barium hydroxide gives two moles of hydroxide in solution then 0.008 moles will give:
Number of moles of
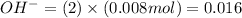 moles
moles
Moles of
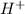 ions in nitric acid
ions in nitric acid
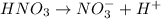
In 1.00 M nitric acid solution
Moles of nitric acid in 1.0 M solution
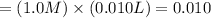 moles
moles
If one mole of nitric acid will give one moles of
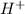 ion.
ion.
Then 0.010 moles of nitric acid in solution will give :
Number of moles of
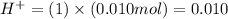 moles
moles
Since , the reaction will be neutralization reaction, equal number of moles of
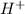 will neutralize equal number of moles of
will neutralize equal number of moles of
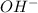
So,0.010 moles of
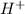 will neutralize 0.010 moles of
will neutralize 0.010 moles of
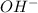 in the solution
in the solution
Remaining moles of
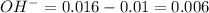 moles
moles
Concentration of
![[OH^-]](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/middle-school/dr3vksfxq7ot5rvw2mjmnw96oc1xtussa2.png) resulting solution
resulting solution
Resulting volume of the solution : 0.004 + 0.010 liters
Calculating
![[OH^-]](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/middle-school/dr3vksfxq7ot5rvw2mjmnw96oc1xtussa2.png) by using equation (1).
by using equation (1).
![[OH^-]=(0.006)/(0.004L+0.010 L)=0.4285 M](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/college/nuin6kzwwty37u9rbisxaoihd08yfbi300.png)
![pOH=-log[OH^-]=-log(0.4285)=0.367](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/college/blrvxd3bj514946197hrdvwrx49h7nz2gf.png)
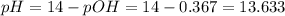
The pH of the solution will be 13.633.