Answer:
If you move a magnet near a coil of wire then the current is induced.
Option A is correct.
Step-by-step explanation:
According to Faraday's law of induction
If we move a magnet near a coil of wire then an emf (electromotive force) is induced in the wire which produces current in it. The induced emf is linked to the rate of change of the magnetic flux linked with the coil.
The induced emf is given by:
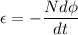
Where,
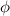 = magnetic flux
= magnetic flux
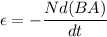
Where, B = magnetic field
A = area of coil
N = number of turns
Hence, If you move a magnet near a coil of wire then the current is induced.