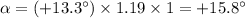Answer:
+15.8°
Step-by-step explanation:
The formula for the observed rotation (α) of an optically active sample is
α = [α]lc
where
l = the cell path length in decimetres
c = the concentration in units of g/100 mL
[α] = the specific rotation in degrees
1. Convert the concentration to units of g/100 mL
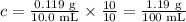
2. Calculate the observed rotation