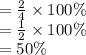Answer:
50%
Step-by-step explanation:
Draw a Punnet square to determine the percentage of offspring that are tall.
The green and blue highlighted columns and rows represents the genotype of the parents. To fill in the genotype of the offspring, write down the letter (T/t) of the parent allele from that row and column the offspring belongs to. By convention, the T is written before t. (The genotype of a tall offspring is written as Tt not tT)
Since the T allele is dominant, as long as the offspring has one T, the offspring is tall. The t allele is recessive, thus two ts (tt) is needed for the short trait to be expressed.
From the Punnet square, the result is 2 offsprings that are tall and 2 offsprings that are short.
Required percentage