Answer : The volume of
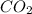 in Reaction 1 = 240.45 ml
in Reaction 1 = 240.45 ml
The volume of
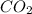 in Reaction 2 = 480.89 ml
in Reaction 2 = 480.89 ml
Solution : Given,
Temperature =
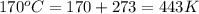 (
(
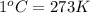 )
)
Pressure = 0.900 atm
The mass of
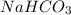 = 1 gram
= 1 gram
Molar mass of
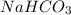 = 84.007 g/mole
= 84.007 g/mole
The given reactions are,
Reaction 1 :
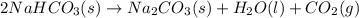
Reaction 2 :
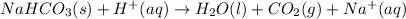
- Calculation for Reaction 1 :
First we have to calculate the moles of
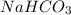 .
.
Moles of
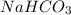 =
=
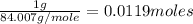
From the Reaction 1, we conclude that
2 moles of
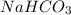 gives 1 mole of
gives 1 mole of
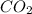
0.0119 moles of
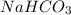 gives
gives
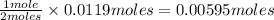 of
of
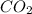
Using ideal gas equation :
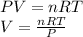
where,
P = pressure of gas
V = volume of gas
n = Number of moles
T = temperature of gas
R = gas constant = 0.0821 L atm/mole K
Now put all the given values in ideal gas law, we get the volume of
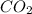
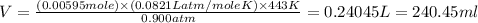
The volume of
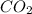 in Reaction 1 is 240.45 ml
in Reaction 1 is 240.45 ml
- Calculation for Reaction 2 :
The moles of
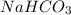 = 0.0119 moles
= 0.0119 moles
From the Reaction 2, we conclude that
1 moles of
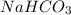 gives 1 mole of
gives 1 mole of
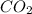
So, the moles of
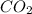 = the moles of
= the moles of
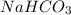 = 0.0119 moles
= 0.0119 moles
Using ideal gas equation,
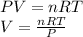
Now put all the given values in ideal gas law, we get the volume of
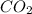
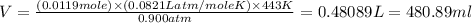
The volume of
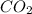 in Reaction 2 is 480.89 ml
in Reaction 2 is 480.89 ml