Answer: Law of Conservation of Mass.
Step-by-step explanation:
Law of Conservation of Mass states that during a chemical reaction mass neither created nor be destroyed or total mass of the reactants is equal to the total mass of the products in balanced chemical equation.
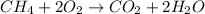
Total mass on the reactant side :
(Mass of one methane molecule + mass of two oxygen molecules)
=
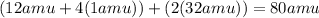
Total mass on the product side :
(Mass of one carbon-dioxide molecule + mass of two molecules of water):
=
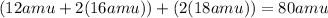
Total mass on the reactant side = Total mass on the product side = 80 u