given that initial speed of the car is
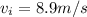
now after travelling the distance d = 1.8 * 10^1 m the car will stop
so here we can use kinematics to find the acceleration of car
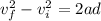
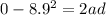
here we have
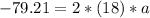
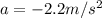
net force applied due to brakes of car is given by Newton's II law
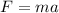
here we have
mass = 1.2 * 10^3 kg
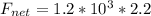
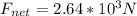
now we can say
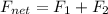
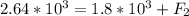

So the force applied due to brakes is given as above