Answer: The definitions and explanation are given below,
Step-by-step explanation:
1. Conditional probability: If we have two events and probability of one event is dependent on other event, then it is known as conditional probability. The conditional probability of two events A and B is defined as
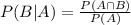 where event A is already occured.
where event A is already occured.
For example: A bag contains 3 red and 4 green balls. Two balls are drawn from the bag. What is the probability of getting red ball after getting green ball.
Independent probability: If we have two events and probability of one event is not dependent on other event, then it is known as independent probability. If the two events A and B are independent then
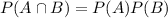 .
.
For example: A bag contains 3 red and 4 green balls. Two balls are drawn from the bag. First ball is drawn, after notice the color of ball we put it into the bag. What is the probability of getting red ball in second drawn.
2. Z-score: The score shows the relation among observation, mean value and standard deviation.

Where, x is observation,
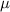 is population mean,
is population mean,
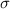 is population standard deviation.
is population standard deviation.
3. Confidence Interval: The interval which defines the observed values are true to the population parameters known as confidence interval. The confidence intervals are defined according to the confidence level. Mostly the confidence level is 95%.
The obervationsare lies outside the confidence interval, then there observations are not true to the population parameters. For 95% confidence level the 5% are know n as error or level of significance.
4. Observational Study: In this method all observations are included in the study like population senses.
Experiments: In this method the treatments applies on a part of population and all observations are not included in the study. For example, samling.
The issues arise during data collection or interpretations are:
i) Duplicacy of data
ii) Irrelevant data provide by the persons
iii) Mistakes made by the person who is collecting the data.
iv) If the purpose of data collection is not clear then the condition of lack of appropriate data occurs.