Answer:
1.3 × 10⁻⁶ atm
Step-by-step explanation:
Let's consider the following reaction at equilibrium.
N₂(g) + O₂(g) ⇄ 2 NO(g)
The equilibrium constant (Kp) is:
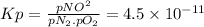
Given pN₂ = 3.00 atm and pO₂ = 0.012 atm, the partial pressure of NO is:
pNO² = Kp × pN₂ × pO₂ = 4.5 × 10⁻¹¹ × 3.00 × 0.012
pNO = 1.3 × 10⁻⁶ atm