Answer:-
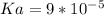
Solution:- percent ionization =
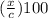
where,
 is the equilibrium concentration of product ion and c is the initial concentration of the acid.
is the equilibrium concentration of product ion and c is the initial concentration of the acid.
Let's plug in the values in the formula:
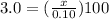
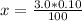
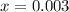
In general, the acid is represented as HA, the ice table is shown as:
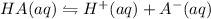
I 0.10 0 0
C -X +X +X
E (0.10 - X) X X
where X is the change in concentration that we already have find out using percentage ionization formula.
![Ka=([H^+][A^-])/([HA])](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/college/ucr9taxm9jzcxnjovkfwkq9esykpuggvin.png)
Let's plug in the values in it:
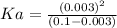
0.003 is almost negligible as compared to 0.10, so (0.10 - 0.003) could be taken as 0.10.
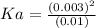
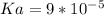
Second choice is the right one.