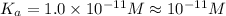Answer: Dissociation constant of the acid is
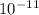 .
.
Step-by-step explanation: Assuming the acid to be monoprotic, the reaction follows:
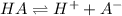
pH of the solution = 6
and we know that
![pH=-log([H^+])](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/college/wil0zflryly1lvza62q3l8chf38jmmfc0c.png)
![[H^+]=antilog(-pH)](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/college/3pejlr5autqsl2pgc2k5tg0kb17v0l6j5c.png)
![[H^+]=antilog(-6)=10^(-6)M](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/college/c5t0959uo6cnhmakyx8vl1opieajockcpo.png)
As HA ionizes into its ions in 1 : 1 ratio, hence
![[H^+]=[A^-]=10^(-6)M](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/college/t7zkpveoibqiqdo50i10vpetr3owdhw86s.png)
As the reaction proceeds, the concentration of acid decreases as it ionizes into its ions, hence the decreases concentration of acid at equilibrium will be:
![[HA]=[HA]-[H^+]](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/college/bdhtwap5fvzw6sqoej8akq94s6paxa7vjm.png)
![[HA]=0.1M-10^(-6)M](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/college/et7uz7bdi8di56uamwrwqcdvty865o5qy6.png)
![[HA]=0.09999M](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/college/afshweu5rky5rdm0t3llko4fqi7vtiae04.png)
Dissociation Constant of acid,
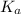 is given as:
is given as:
![K_a=([A^-][H^+])/(HA)](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/college/325mjc7mxlzxn5wxa5lyznqf5kxq2fgjkn.png)
Putting values of
![[H^+],[A^-]\text{ and }[HA]](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/college/wdgfyt01mm3z20w5bd9v1ek1rx1ng9fwb2.png) in the above equation, we get
in the above equation, we get
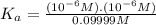
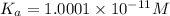
Rounding it of to one significant figure, we get