The particle has acceleration vector
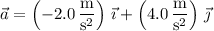
We're told that it starts off at the origin, so that its position vector at
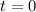 is
is
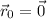
and that it has an initial velocity of 12 m/s in the positive
 direction, or equivalently its initial velocity vector is
direction, or equivalently its initial velocity vector is
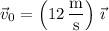
To find the velocity vector for the particle at time
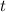 , we integrate the acceleration vector:
, we integrate the acceleration vector:
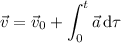
![\vec v=\left[12\,(\mathrm m)/(\mathrm s)+\displaystyle\int_0^t\left(-2.0\,(\mathrm m)/(\mathrm s^2)\right)\,\mathrm d\tau\right]\,\vec\imath+\left[\displaystyle\int_0^t\left(4.0\,(\mathrm m)/(\mathrm s^2)\right)\,\mathrm d\tau\right]\,\vec\jmath](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/physics/middle-school/crp17xql5jt7k4ncjk8l6ux1g4jmwjdoww.png)
![\vec v=\left[12\,(\mathrm m)/(\mathrm s)+\left(-2.0\,(\mathrm m)/(\mathrm s^2)\right)t\right]\,\vec\imath+\left(4.0\,(\mathrm m)/(\mathrm s^2)\right)t\,\vec\jmath](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/physics/middle-school/he1wam86i16s82y0hdgpadvu8jpmxdaogt.png)
Then we integrate this to find the position vector at time
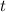 :
:
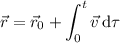
![\vec r=\left[\displaystyle\int_0^t\left(12\,(\mathrm m)/(\mathrm s)+\left(-2.0\,(\mathrm m)/(\mathrm s^2)\right)t\right)\,\mathrm d\tau\right]\,\vec\imath+\left[\displaystyle\int_0^t\left(4.0\,(\mathrm m)/(\mathrm s^2)\right)t\,\mathrm d\tau\right]\,\vec\jmath](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/physics/middle-school/qs1cnj8boi0yolx8d1bsidpbrtkp9ymw9b.png)
![\vec r=\left[\left(12\,(\mathrm m)/(\mathrm s)\right)t+\left(-1.0\,(\mathrm m)/(\mathrm s^2)\right)t^2\right]\,\vec\imath+\left(2.0\,(\mathrm m)/(\mathrm s^2)\right)t^2\,\vec\jmath](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/physics/middle-school/mcyiucjmrrvw3mlhk1faz33byyu562v8gw.png)
Solve for the time when the
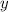 coordinate is 18 m:
coordinate is 18 m:
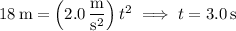
At this point, the
 coordinate is
coordinate is
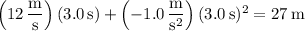
so the answer is C.