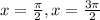we are given
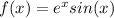
(a)
Firstly, we will find critical numbers
so, we will find derivative
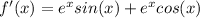
now, we can set it to 0
and then we can solve for x
we get
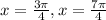
now, we can draw a number line and then locate these values
and then we can find sign of derivative on each intervals
increasing intervals:
![[0,(3\pi)/(4) )U((7\pi)/(4) , 2\pi]](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/mathematics/middle-school/o27pprpyjlmsx1p392l26r7bwusp7odb00.png)
Decreasing interval:
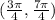
(b)
Local maxima:
It is the value of x where function changes from increasing to decreasing
so, local maxima is at
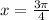
Local minima:
It is the value of x where function changes from decreasing to increasing
so, local minima is at
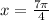
now, we will plug critical numbers and end values into original function
and we get
At x=0:
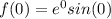
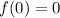
At
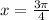 :
:
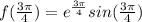
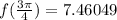
At
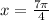 :
:
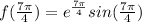
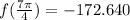
At
 :
:
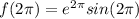
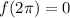
Global maxima:
It is the largest value among them
so, we get
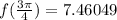
Global minima:
It is the largest value among them
so, we get
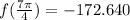
(c)
now, we can find second derivative
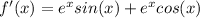
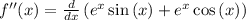
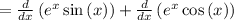
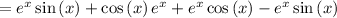
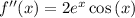
now, we can set it to 0
and then we can solve for x
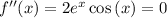
so, we get
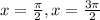
now, we can draw number line and locate these values
and then we can find sign of second derivative on each intervals
concave up intervals:
![[0,(\pi)/(2))U((3\pi)/(2), 2\pi]](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/mathematics/middle-school/wpi46otonrvdt3elxjlpfd9xpxm3lvg26o.png)
Concave down intervals:
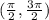
Turning points:
All values of x for which concavity changes
so, we get turning points at