1. D) decreases, inverse
The average speed for each lap is given by:
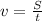
where S is the length of the lap (400 m) while t is the time taken to complete the lap. Since the time t increases at each lap, we see from the formula that v, the speed, decreases at each lap. This is an example of inverse relationship: when one of the two quantities increases (the time), the other one decreases (the speed).
2. A) Velocity on the y-axis, time on the x-axis
Acceleration is defined as the change in velocity divided by the time taken:
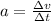
In a graph, the slope of a line is given by the increment in y divided by the increment in x:
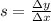
Therefore, if we put velocity on the y-axis and time on the x-axis, we immediately see that the acceleration corresponds to the slope of the curve.
3. D) velocity
In fact, velocity consists of 1) speed and 2) direction. The speed can be calculated as:
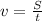
where S is the distance covered and t the time taken. So, by knowing these two quantities, Tim can calculate the speed of the trip. Tim also knows the direction of motion, so he can determine the velocity of the trip.
4. B) equal, different
The difference between speed and velocity is simple: speed is a scalar, and it is just the magnitude of the velocity, so "how fast" is the object moving, while velocity takes also into account the direction of motion, so it is a vector.
Therefore: the two cars have same speed (25 m/s), but they have different velocities, since they are moving into different directions (car A is moving from NY to Miami, while car B is moving from NY to Chicago).
28. B) 11 m
The distance travelled by the bag in free fall is given by:
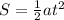
where
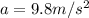 is the acceleration of gravity and t=1.5 s is the time. Replacing these numbers into the formula, we find
is the acceleration of gravity and t=1.5 s is the time. Replacing these numbers into the formula, we find
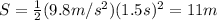
29. B) 10 m/s south
The boat is moving 20 m/s south, relative to the ground. The passenger is moving 10 m/s north, relative to the boat. Considering south as positive direction, the passenger's velocity relative to the ground is
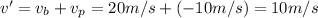
and the positive sign means it is due south.
30. B) direction
In fact, velocity is a vector, so it consists of a magnitude (the speed) and a direction. The speed can be determined by the distance and the time, in fact speed is defined as
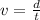
where d=distance and t=time; however, in order to determine velocity, we also need to know the direction of motion.
33. B) a velocity.
In fact, velocity is a vector, and it consists of a magnitude (the speed) and a direction. In this case, 10 m/s is the speed, while north is the direction.
34. C) Does the measurement include direction?
As stated in the previous question, a vector includes both magnitude and direction, while a scalar includes only a magnitude. Therefore, by asking if the measurement includes a direction, we are able to determine if the quantity is a vector or not.