Answer: The new pressure of the gas is (A) 854.46 kPa.
The pressure of a given mass of gas at the absolute temperature 110 degrees K is 400 kPa.
The temperature is raised to 235 degrees K with constant volume.
Therefore,
Initial pressure
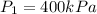
Initial temperature
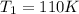
Final temperature
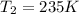
Final pressure
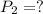
According to pressure law of gas,
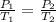 ( at constant volume)
( at constant volume)
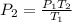
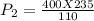
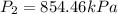
Thus, the required new pressure of the gas is 854.46 kPa.