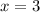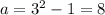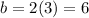Using the Pythagorean Theorem,
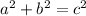
(See attachment)
Let us substitute the values and solve for b in terms of
 .
.
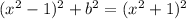
Grouping the
 terms on one side gives,
terms on one side gives,
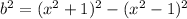
We now apply difference of two squares to obtain,
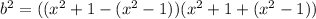
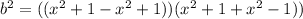
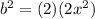
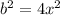
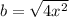
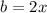 ,
,
Testing for some few values greater than 1, we can generate the Pythagorean triples as follows;
When
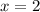
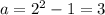
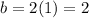
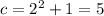
When