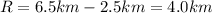The maximum magnitude of their resultant vector is when the two vectors are parallel and in the same direction, so they lie on the same axis. In this case, the magnitude of their resultant vector is simply the sum of the two magnitudes:
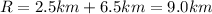
The minimum magnitude of their resultant vector is when the two vectors are parallel but in opposite direction. In this case, the magnitude of their resultant vectors is just the difference between the two magnitudes: