Here it is given that speed of migrating Robin is 12 m/s relative to air
so we can say that
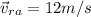 North
North
so it will be
Let North direction is along Y axis and East direction is along X axis
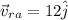
also it is given that speed of air is 6.7 m/s relative to ground
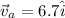
now as we know by the concept of relative motion
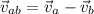
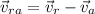
now by rearranging the terms
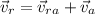
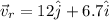
now we need to find the speed of Robin which means we need to find the magnitude of its velocity which we found above
So here we will say
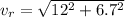
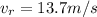
so the net speed of Robin with respect to ground will be 13.7 m/s